 Happy dance! I just learned there are different types of magnesium and there’s a specific one for me. See below to see if one might benefit you. It took me awhile to figure out I had a deficiency since I didn’t recognize the symptoms. A sleep disorder from an old head injury alternates me between insomnia and hypersomnia so I can’t always tell if I’m sleepy or if I’m fatigued. I’ve had the fatigue 20+ years and have learned it doesn’t matter if I lie around and do nothing or if I run around and do everything I need to do. I discovered I don’t feel any more fatigued when I run around, so I make myself do it.
Happy dance! I just learned there are different types of magnesium and there’s a specific one for me. See below to see if one might benefit you. It took me awhile to figure out I had a deficiency since I didn’t recognize the symptoms. A sleep disorder from an old head injury alternates me between insomnia and hypersomnia so I can’t always tell if I’m sleepy or if I’m fatigued. I’ve had the fatigue 20+ years and have learned it doesn’t matter if I lie around and do nothing or if I run around and do everything I need to do. I discovered I don’t feel any more fatigued when I run around, so I make myself do it.
That’s an Aries for you. Aries is the head and I know the mind directs the body. This body WILL do what I want it to do, In return I’ll give it nutritious fuel, I’ll keep it moving and fit and I’ll give it enough rest. It’s powerful being in charge of this entire physical body and knowing it’s all up to me how long and well it’s able to keep going. It works when I work it! I first heard about magnesium supplementation when I was researching Adrenal Fatigue. Then I found it could help my injured knee. In three months, my knee was healed and I wasn’t experiencing fatigue. I stopped taking it and I once again experienced fatigue. I began again and it abated. I went to order more and wanted to try tablets, since I was using the oil. I learned there were different types of magnesium. I ordered the magnesium malate which targets fatigue. Check out below to see if you might benefit from some form of magnesium.
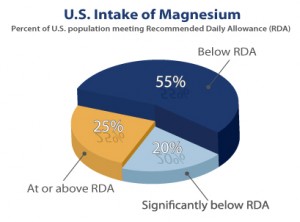
(NaturalNews) According to the American Chiropractic Society, an estimated 68 to 80 percent of the United States population is deficient in the essential mineral magnesium. While our growing dependence on processed food is partly responsible for this alarming statistic, the real reason for it is that ongoing soil erosion has significantly depleted the mineral content of our soil within the last century. Consequently, many fruits and vegetables that were once rich in magnesium no longer contain it in adequate amounts, resulting in widespread deficiencies.
For this reason, an increasing number of people are turning to magnesium supplements to boost their intake of this vital nutrient. However, since magnesium must be bound to another substance before it can be adequately absorbed, magnesium supplements come in a number of different forms that provide different, or targeted, health benefits. This article takes a closer look at the best (and worst) forms of magnesium on the market today.
The best forms of magnesium:
Magnesium citrate — Magnesium citrate is the most popular magnesium supplement, probably because it is inexpensive and easily absorbed. Since citric acid is a mild laxative, magnesium citrate functions as a constipation aid as well as a magnesium source. It is a great choice for individuals with rectal or colon problems but is unsuitable for those with loose bowel movements.
Magnesium taurate — Magnesium taurate is the best choice of magnesium supplement for people with cardiovascular issues, since it is known to prevent arrhythmias and guard the heart from damage caused by heart attacks. Magnesium taurate is easily absorbed (magnesium and taurine stabilize cell membranes together), and it contains no laxative properties.
Magnesium malate — Magnesium malate is a fantastic choice for people suffering from fatigue, since malic acid — a natural fruit acid present in most cells in the body — is a vital component of enzymes that play a key role in ATP synthesis and energy production. Since the ionic bonds of magnesium and malic acid are easily broken, magnesium malate is also highly soluble.
Magnesium glycinate — Magnesium glycinate (magnesium bound with glycine, a non-essential amino acid) is one of the most bioavailable and absorbable forms of magnesium, and also the least likely to induce diarrhea. It is the safest option for correcting a long-term deficiency.
Magnesium chloride — Though magnesium chloride only contains around 12 percent elemental magnesium, it has an impressive absorption rate and is the best form of magnesium to take for detoxing the cells and tissues. Moreover, chloride (not to be confused with chlorine, the toxic gas) aids kidney function and can boost a sluggish metabolism.
Magnesium carbonate — Magnesium carbonate is another popular, bioavailable form of magnesium that actually turns into magnesium chloride when it mixes with the hydrochloric acid in our stomachs. It is a good choice for people suffering from indigestion and acid reflux, since it contains antacid properties.
The worst forms of magnesium
Magnesium oxide — Magnesium oxide is the most common form of magnesium sold in pharmacies, but it is non-chelated and possesses a poor absorption rate compared to those listed above.
Magnesium sulfate — Magnesium sulfate, also called Epsom salt, is a fantastic constipation aid but an unsafe source of dietary magnesium, since overdosing on it is easy.
Magnesium glutamate and aspartate — Avoid these two forms of magnesium completely. Glutamic acid and aspartic acid are components of the dangerous artificial sweetener aspartame, and both of them become neurotoxic when unbound to other amino acids.
About the author:
Michael Ravensthorpe is an independent writer whose research interests include nutrition, alternative medicine, and bushcraft. He is the creator of the website, Spiritfoods, through which he promotes the world’s healthiest foods.
Sources for this article include:
http://www.metabolics.com
http://www.medhelp.org
http://drsircus.com
http://afibbers.org [PDF]
http://www.metabolics.com
http://science.naturalnews.com
RELATED: Magnesium Chloride for Health and Rejuvenation
Magnesium Oil Benefits and How I Healed My Knee
